HAND BOOK
OF
TEXTILE PHYSICS
EIDIT BY
SALAUDDIN FERDOUS
&
RAKIB HASAN
Tensile properties of textile material
1. Tenacity
2. Breaking extension
3. Work of rupture
4. Initial modulus
5. Work factor
6. Work recovery
7. Elastic recovery
8. Yield stress
9. Yield strain
10.Yield point
11. Breaking load
12. Creep
1. Tenacity: The ratio of load required to break the specimen and the linear density of that specimen is called tenacity.
Mathematically, Tenacity = Load required to break the specimen / Linear density of the specimen
Unit: gm/denier, gm/Tex, N/Tex, CN/Tex etc.
2. Breaking extension: The elongation necessary to break a textile material is a useful quantity. It may be expressed by the actual percentage increase in length and is termed as breaking extension.
Mathematically, Breaking extension (%) = (Elongation at break / Initial length) × 100%
3. Work of rupture: Work of rupture is defined as the energy required to break a material or total work done to break that material.
Unit: Joule (J)
4. Initial modulus: The tangent of angle between the initial curve and the horizontal axis is equal to the ratio of stress and strain.
In engineering science the ratio is termed as Young’s Modulus and in textile we use the terms as Initial Young’s Modulus.
Initial modulus, tan α = stress / strain
Tan α ↑↓ → extension ↓↑
5. Work factor: The ratio between work of rupture and the product of breaking load and breaking elongation is called work factor.
Work factor = work of rupture / (breaking load × breaking elongation)
6. Work recovery: The ratio between work returned during recovery and total work done in total extension is called work recovery.
Total extension = Elastic extension + Plastic extension
Total work = work required to elastic extension + work required to plastic extension.
7. Elastic recovery: the power of recovery from a given extension is called elastic recovery. Elastic recovery depends on types of extension, fiber structure, types of molecular bonding and crystalline of fiber.
Here, AB = initial length of the specimen
AB = final length after recovery
BD = total extension
CD = elastic extension
BC = plastic extension
Total extension = Elastic extension + Plastic extension
So,
Elastic recovery (%) = (Elastic extension/total extension) ×100%
= (CD/BD) × 100%
So,
Plastic recovery = (plastic extension/total extension) ×100%
= (BC/BD) ×100%
# Stress-strain curve
When fiber is deformed then the fiber follows the stress-strain curve.
Here, A to B → linear region. This region follows Hook’s law (stress ∞ strain). So, fiber comes to its original position after removal of load. So, the region is called elastic region and the deformation is called elastic deformation.
B to C → plastic region. In this region chain breaks but fiber do not break. Here the deformation is known as plastic deformation.
C → Breaking point. The fiber will be break at this point.
8. B → Yield point. The point up to which a fiber behaves elastic deformation and after which a fiber shows plastic deformation is called yield point.
9. Yield stress → The stress at yield point is called yield stress.
10. Yield strains: The strain at yield point is called yield strain.
11. Breaking load: The load which is required to break a specimen is called breaking load.
12. Creep: when a load is applied on the textile material an instantaneous strain is occurred, but after that the strain will be lower with the passing time. This behavior of the material is termed as creep.
There are two types of creep:
i. Temporary creep
ii. Permanent creep
Difference between temporary and permanent creep:
| i. Recoverable | i. Non recoverable. |
| ii. Textile material comes back to its original position after removal of load. | ii. Textile material does not come back to its original position after removal of load. |
| iii. Elastic extension occurs. | Plastic extension occurs. |
| iv. Polymer chains slightly stretch. | iv. Polymer chains break. |
Factors determined the result of tensile experiment:
1. The material and its condition-
a. The chemical treatment to which it has been subjected
b. The mechanical treatment that it has been received
c. On the amount of moisture that it contains
d. On the temperature
2. The arrangement and dimension of the specimen.
3. The nature and timing of the test.
Principles of tensile experiment or Method of tensile experiment:
1. CRL method ( constant rate of loading )
2. CRE method (constant rate of elongation)
1CRL method: The function of applied force is to extent the specimen until it eventually breaks down. Here the loading causes the elongation.
By adding constant rate of water flow in a container which is attached with the jaw J2 may increase the load gradually. Thus constant rate of flow gives constant rate of loading.
2.CRE method: A specimen A is gripped between two jaws. J1 is fixed and bottom jaw J2 is movable to down-ward at constant velocity by mean of a screw mechanism. Initially the tension on A is zero. But when the bottom jaw J2 moves down-ward at a constant rate the specimen is extended and an increasing tension is developed until it eventually breaks down. Here the elongation /tension causes loading.
Difference between CRL & CRE methods:
| 1. CRL means Constant rate of loading. | 1. CRE means Constant rate of elongation. |
| 2. This method contains container and water flow used to increase load gradually. | 2. This method contains screw mechanism. |
| 3. In this method loading causes elongation. | 3. In this method elongation/ extension causes loading. |
Types of tensile strength testing instruments:
-For CRL principle:
i. The Cambridge extensometer
ii. Scott inclined plane tester
iii. Kari’s instrument
iv. Pressley fiber strength tester
-For CRE principal:
i. The Cambridge extensometer
ii. Inston tensile tester
iii. Pendulum lever machine
Tensile properties of different fibers:
| Fiber | Tensile(N/Tex) | Breaking extension (%) |
| Cotton | 0.19-0.45 | 5.6-7.1 |
| Jute | 0.31 | 1.8 |
| Silk | 0.38 | 23.4 |
| Nylon | 0.47 | 26 |
| Polyester | 0.47 | 15 |
| Wool | 0.11-0.14 | 29.8-42.9 |
Flexural property
The behavior which shows by textile material during bending is called flexural property.
1. Flexural rigidity
2. Bending recovery
3. Bending modulus
1. Flexural rigidity: Flexural rigidity is the stiffness of a textile fiber. It can be defined as the couple needed to bend a fiber.
Mathematically,
Flexural rigidity = (1/4π) (ηET2/ρ)
Where, η = shape factor, E = specific shear modulus, T =linear density (Tex), ρ = density (gm/cm3)
Specific flexural rigidity: Specific flexural rigidity can be defined as the flexural rigidity of linear density.
Mathematically,
Specific flexural rigidity = (1/4π)(ηE/ρ)
Where, η = shape factor, E = specific shear modulus, ρ = density (gm/cm3)
2. Bnding recovery: The recovery from a given curvature is called bending recovery.
Say, nylon shows 100% recovery from small curvature of 15D, where it shows 20% recovery from large curvature.
Unit = N-m2/ Tex.
3. Shape factor: shape factor is a number that indicates the shape of a fiber. Shape is expressed by “η”.
If, η = 1, it indicates the shape of fiber is round.
If, η > 1, it indicates the shape of fiber is increased.
If, η < 1, it indicates the shape of fiber is decreased.
Torsional property
The behaviors which are shown by a textile material when it is subjected to a torsional force is called torsional property.
1. Torsional rigidity
2. Breaking twist
3. Shear modulus
1. Torsional rigidity: Torsional rigidity can be defined as the torque required against twisting is done for which torque is termed as torsional rigidity.
Mathematically, torsional rigidity = ηET2/ρ
Where, η = shape factor, E = specific shear modulus (N/tex)
Specific torsional rigidity: Specific torsional rigidity can be defined as the torsional rigidity of a fiber of unit linear density.
Mathematically, specific torsional rigidity = ηE/ρ
Unit: N-m2 /Tex
2. Breaking twist: The twist for breaking of a yarn is called breaking twist. It also can be defined as the number of twists required to break a yarn. Breaking twist depends on the diameter of fiber and it is inversely proportional to its diameter.
That is, Tb ∞ 1/d
Where, Tb = Breaking twist, d = diameter of fiber
Breaking twist angle: This is the angle through which outer layer of fiber are sheared at breaking.
Mathematically, α = tan-1(πdTb)
Where, α = breaking twist angle, d = diameter of fiber, Tb = breaking twist per unit length
Breaking twist angle of different fibers:
| Fiber | Breaking twist angle (α) |
| Cotton | 35* |
| Viscose | 33* |
| Polyester | 50* |
| Wool | 40* |
| Silk | 39* |
| Glass | 4* |
3. Shear modulus: Shear modulus is defined as the ratio of shear stress & shear strain. Shear modulus is measured in radians.
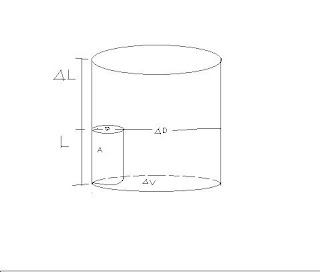
11. Transverse dial swelling: Fractional increase in diameter of a fiber after swelling is called transverse dia swelling. Mathematically,
Transverse dia swelling, SD = ∆D / D
Where, D = original diameter of fiber, ∆D =increased diameter of swollen fiber.
2. Transverse area swelling: Fractional increase in area of a fiber after swelling is called transverse area swelling.
Mathematically,
Transverse area swelling, SA = ∆A / A
Where, A = original area of fiber, ∆A =increased area of swollen fiber.
3. Axial swelling: Fractional increase in length of a fiber after swelling is called axial swelling.
Mathematically, Axial swelling, SL = ∆L / L
Where, A = original length of fiber, ∆L =increased length of swollen fiber.
4. Volume swelling: Fractional increase in volume of a fiber after swelling is called volume swelling.
Mathematically,
Volume swelling, SV = ∆V / V
Where, V = original Volume of fiber, ∆V =increased volume of swollen fiber.
Relation between SA & SD:
We know that,
Transverse area swelling, SA = ∆A / A
Transverse dia swelling, SD = ∆D / D
For a circular fiber, area A = (π/4)D2
For a swollen fiber, we get, A+∆A = (π/4)(D+∆D)
= (π/4)(D2 + 2D. ∆D + ∆D2)
Now,
SA = ∆A / A
= (A+∆A-A) / A
= {(π/4) (D2 + 2D. ∆D + ∆D2) - (π/4) D2}/ (π/4) D2
= (π/4) (D2 + 2D. ∆D + ∆D2 - D2) / (π/4) D2
= (2D. ∆D + ∆D2) / D2
= (2D. ∆D / D2) + (∆D2/ D2)
= 2(∆D / D) + (∆D2/ D2)
= 2 SD + SD2
So, SA = 2 SD + SD2.
Relation between SA ,SV & SL:
We know that,
Transverse area swelling, SA = ∆A / A
Volume swelling, SV = ∆V / V
Axial swelling, SL = ∆L / L
For a circular fiber, volume, V=AL
For a swollen fiber, we get, V +∆V = (A +∆A )(L +∆L)
= AL + A∆L + ∆AL + ∆A ∆L
Now, SV = ∆V / V
=(V+ ∆V - V) / V
=( AL + A∆L + ∆AL + ∆A ∆L - AL)/AL
= ∆L / L+ ∆A/ A + ∆A/ A. ∆L / L
= SL + SA + SL. SA
So, SV = SL + SA + SL. SA.
Frictional Property
When the textile materials are processed, then friction is developed between the fibers. The properties which are shown by a textile material during friction is known as frictional property.
Frictional properties depend on-
1. Composition of the material
2. State of the surface of the material
3. Pressure between the surfaces
4. Temperature
5. Relative humidity %
Co-efficient of friction:
Frictional force is proportional to the normal or perpendicular of a material due to its own weight.
That is, F ∞ N
Or, F = μ N
Or, μ = F/N
Where, F = Frictional force, N = Normal / perpendicular force
Here, μ is the proportional constant known as “co-efficient of friction”.
So, co-efficient of friction can be defined as the ratio of frictional force and perpendicular force.
Methods of measuring co-efficient of friction:
Capstan method is most commonly used to measure co-efficient of fraction. Capstan method can be classified into two classes-
1. Static capstan method
2. Dynamic capstan method
Other methods-
1. Buckle & Pollitt’s method
2. Abboh & Grasberg method
3. Gutheric & Olivers method
Influences of friction on textile material:
· Friction holds the fibers in a sliver and hence the sliver does not break due to its’ own weight.
· Friction helps in drafting and drawing.
· Uniform tension can be maintained during winding & warping because of friction.
· Friction helps to make yarn by twisting during spinning.
· Friction increases lusture and smoothness of the yarn and the fabric.
· Friction makes more clean material.
Demerits of friction on textile material:
· Friction causes nap formation.
· High static friction causes high breakage of yarn during weaving.
· If the frictional force is high, the handle properties of fabric will be low.
· Friction generates temperature and therefore static electricity is developed which attracts dust, dirt etc. and the materials become dirty.
· Sometimes due to over friction materials may be elongated.
· Friction increases yarn hairiness.
· Friction worn out parts of machine.
Minimization of friction intensity:
1. Sizing is done in warp yarn before weaving to reduce frictional intensity. As a result, yarn damage will be reduced.
2. Emulsion, oil, lubricants etc. are specially applied on jute fiber to reduce friction.
3. Chemical treatment is done on wool fiber to reduce scale sharpness and thus reduce friction during processing.
4. By calendaring frictional intensity of cloth is reduced.
5. Sometimes resin finish is applied on fabric to reduce friction.
PYSICAL STUCTURES OF FIBRE
Requirement of fiber formation or fiber forming polymer:
1) Polymer should have long & linear chain molecules.
2) They must be chemically resistance.
3) Molecular chain must be parallel to each other.
4) They should have attractions.
5) Some measures of freedoms of molecules movement due to give required extensibility.
6) Lateral forces to hold the molecules together and gives cohesion the structure.
Methods of fiber structure investigation:
1) X-ray diffraction method
2) Infra-red radiation method
3) Electron microscopic method
4) Optical microscopic method
5) Thermal analysis
6) Nuclear magnetic resonance methods
7) Density
8) General physical properties
9) The chemistry of fiber material
Properties of x-ray diffraction method:
1) Determination of chemical groups
2) Determination of molecular spacing
3) Determination of chemical bonding
4) Determination of degree of crystallinity & orientation
5) Determination of water absorption
Properties of Infra- red radiation absorption method:
1) Determination of spiral turns or convolution of cotton fiber
2) Determination of molecular spacing
3) Determination of chemical bonding
4) Determination of degree of crystallinity & orientation
5) Determination of molecular packing
6) Determination of cross-sectional shape of fiber
7) Identifications of fiber
Crystallinity:
Crystallinity is the arrangement of fiber molecules in the molecular chain.
Properties of crystallinity:
1) More dense
2) More stiff
3) More strength
4) More rigid
5) Less water absorbent
Measurement of crystallinity:
1) X-ray diffraction method
2) Infra-red radiation absorption method
3) Density measurement methods
Orientation:
Orientation is the arrangement of molecular chain of fiber.
Properties of Orientation:
1) More dense
2) More stiff
3) More strength
4) More rigid
5) More water absorbent
6) More lustrous
7) Less elastic as less extension
Measurement of Orientation:
1) X-ray diffraction method
2) Infra-red radiation absorption method
3) Density measurement methods
Effects of structural factors on fiber properties:
1) Chemical bonding:
a) Single bond
-More strength, less flexibility
b) Double bond
- Less strength, more flexibility
2) Character of polymer chin:
a) Long chain, such as [-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-]n
-More strength, less flexibility
b) Sort chain, such as [-CH2-CH2-]n
-Les strength, more flexibility
c) Long side chain
-More strength, less flexibility
d) Sort side chain
-Less strength, more flexibility
3) Molecular packing:
a) Regular packing:
CH3 CH3
׀ ׀
-CH2-C-CH2-C-CH2-
׀ ׀
CH3 CH3
-More strength, less flexibility
b) Irregular packing:
CH3
׀
N H-C-H
׀ ׀
-CH2-C-CH2-C-CH2-
׀ ׀
CH3 CH3
-Less strength, more flexibility
4) Crystallinity:
High crystallinity, higher strength and less flexibility
5) Orientation:
High Orientation, higher strength and less flexibility
6) Nature of monomer:
a) Same monomer (Homopolymer)
-More strength, less flexibility
b) Same monomer (Co-polymer)
-Less strength, more flexibility
7) Internal structure of fiber polymer:
a) For ring structure
-More strength, less flexibility
b) For normal structure
-Less strength, more flexibility
THERMAL PROPERTY]
Thermal property:
The property which is shown by a textile fiber when it is subjected to heating is called thermal property.
Thermal properties are including:
1. Thermal conductivity
2. Heat of wetting or heat of absorption
3. Glass transition temperature
4. Melting temperature
5. Heat setting
6. Thermal expansion
Ø Thermal conductivity:
Thermal conductivity is the rate of heat transfer in degree along the body of a textile fiber by conduction.
Higher the thermal conductivity indicates the fiber more conductive.
Thermal conductivity is measure by co-efficient of thermal conductivity.
Ø Heat of wetting:
When a textile fiber absorb moisture or water it gives of some amount of heat which is called heat of wetting or heat of absorption. Heat of absorption resulting from changes in moisture regain rather than the thermal conductivity.
If 1gm of dried textile fiber is completely wetted then heat in calory/gm is involved which is known as heat of wetting for that fiber.
Ø Glass transition temperature(Tg):
The temperature up to which a fiber behaves hard as like glass and after which it behaves soft as like rubber is called Glass transition temperature and it is denoted by Tg.
The range of Tg is lies between -100˚C to 300˚C
Ø Melting temperature:
A temperature at which fiber melt completely is called melting temperature.
At melting temperature fiber losse its identity and convert it into a viscous liquid.
At melting temperature fiber also losse its strength and some molecular weight.
Ø Thermal expansion:
Thermal expansion can be measured by co-efficient of thermal expansion and which is defined as the fractional increase in length of a specimen to rise in temperature by 1˚C.
Co-efficient of thermal expansion
═ Length increased / initial length of specimen
═ ∆L / L
═ L2-L1 / L1
Ø Heat setting:
Heat setting is the process of stabilizing the form of fibers, yarns, fabric or garment by means of successive heating or cooling in dry and wet condition.
| Fiber | Tg(˚C) | Tm(˚C) |
| Polyester | 64 | 269 |
| PVC | 81 | 310 |
| PAN | 97 | 314 |
| Rubber | - | 36 |
| Tri-acetate | 73 | 306 |
| Nylon-6 | 50 | 250 |
| Nylon 6:6 | 50 | 270 |
Static electricity
Static electricity:
If two surfaces come in close contact with each other, then charge is created due to friction between them. The produced charge remains enclosed and static in those surfaced. They can not move from one place to another place. Here only charges are exchanged between two surfaces. This type of electricity is called static electricity.
Problem caused by static electricity in textile:
1. Similar charge repel each other:
a) The filament in a charged warp will blow out away from one another.
b) This causes difficulties in handling materials.
c) There will be ballooning of a bundle of sliver.
d) Cloth will not fold down neatly upon itself when it comes off a finishing machine.
2. Different charge attracts each other:
a) Difficulties in the opening of the parachute.
b) Different parts of garments may be stick together.
3. Attraction between charged particles & charged textile materials:
a) Roller lapping may occur.
b) Dust, Dirt’s etc may be attracted by the textile material as a result materials become dirt.
c) Soiling of cloth may occur.
d) Fibers may stick to the earthed parts of the machine.
Methods of minimizing static electricity:
v By using conducting liquids like emulsion, oil, friction between the materials ca be reduced as a result, static electricity will be minimize.
v By increasing relative humidity of the atmosphere, static electricity can be minimized.
v By using anti-static agent on the materials static problem may reduce.
v By ear thing the metallic part of the machinery static electricity can be minimized.
v By blending conductive materials with non conductive materials, static electricity can be minimized.
Fiber migration:
Migration occurs during spinning both in staple and filament yarns. The effect of migration is more pronounced in staple yarn than in filament yarn. The migration of fiber affect on many properties of fiber as like elongation and strength.
According to the textile institute “The change in the distance of a fiber or filament form the axis of a yarn during production is called fiber migration.







 9:45 PM
9:45 PM
 TextileBd
TextileBd